April 2025
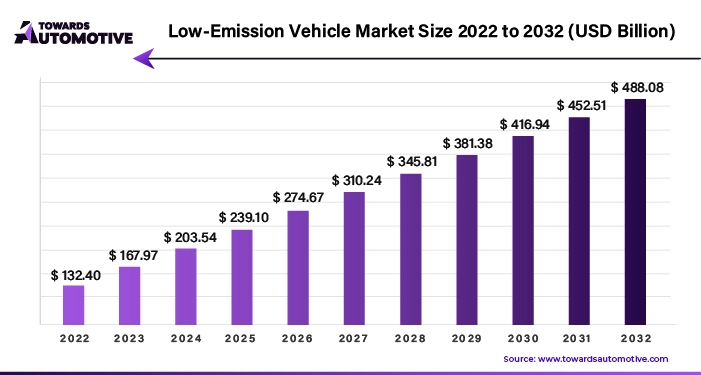
The low-emission vehicle market is projected to reach USD 618.45 billion by 2034, growing from USD 212.89 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 12.58% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Unlock Infinite Advantages: Subscribe to Annual Membership
The COVID-19 pandemic wrought havoc on the transportation sector, compelling nearly 95% of transportation companies to enact widespread layoffs during the shutdown period. This unprecedented disruption reverberated across the global automotive industry, resulting in significant production halts and economic turmoil. However, as the global economy gradually reopens and automobile production resumes, the market is witnessing a resurgence in strength.
Looking ahead, government policies aimed at bolstering the growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and expanding electric vehicle charging infrastructure are poised to exert a significant influence on commercial dynamics throughout the forecast period. Numerous companies within the sector have unveiled ambitious plans to incorporate electric vehicles into their product portfolios, foreseeing a notable share of new car sales in the coming years.
Projections indicate that electric car sales will surge to 3 million units in 2020, representing a remarkable 40% increase compared to 2019 figures. This robust growth trajectory stands in stark contrast to the broader decline observed in the global car market, which experienced a 16% downturn due to the COVID-19 crisis. Over the past decade, the number of electric cars in operation has surpassed 10 million, accounting for approximately 1% of the global car fleet. Looking ahead to 2030, the "2050 Net Zero Emissions" scenario envisages a staggering 300 million electric cars on the road, constituting over 60% of new car sales, a significant leap from the 4.6% share recorded in 2020. Initial market reports for 2021 suggest a continued rapid expansion in the core electric vehicle segment.
The electric vehicle (EV) market has witnessed substantial growth driven by the imperative to address future energy requirements. Efficient transportation is deemed critical to meeting escalating electricity demands, further fueling the growth of the EV sector.
Emerging as a pivotal component of the automotive industry, the electric vehicle sector embodies a pathway to achieving energy efficiency objectives and curbing emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases. Escalating environmental concerns and proactive government interventions are among the key drivers propelling economic expansion in this domain. Moreover, the surge in energy prices and intensifying competition in new energy technologies are poised to underpin market growth, fostering ongoing investment and innovation in the electric vehicle landscape.
Electric vehicle sales are significantly influenced by environmental policies implemented by various countries. Leading nations in electric vehicle adoption, such as China, the USA, Norway, Germany, Japan, the UK, France, Sweden, Canada, and the Netherlands, have introduced a range of policies to stimulate vehicle sales. These measures include public procurement initiatives, financial incentives to promote the production and purchase of electric vehicles, and incentives to reduce operating costs, such as free parking privileges.
Regulations at different levels of government, such as fuel economy standards and emission-based traffic restrictions, also play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape. For instance, Bharat Stage (BS) standards in India aim to tighten regulations by lowering permissible pollutant emission levels. The transition from BS-IV to BS-VI standards, effective from 2020, significantly reduced sulfur emissions to 10 parts per million (ppm), among other stringent requirements.
India's FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacture of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) and FAME II policies offer attractive incentives for investors and companies to establish electric vehicle manufacturing facilities, thereby accelerating the adoption of green vehicles. In many cities and countries, public transportation fleets are being electrified with the help of government subsidies. For instance, India aims to deploy nearly a thousand electric buses for public transportation by 2021, with Mumbai leading the country with 246 electric buses.
Thailand has embarked on an ambitious plan to establish a widespread electric vehicle charging infrastructure, with the goal of deploying 53,000 electric motorcycles and 5,000 electric buses by the end of 2022 and 2025, respectively. The Asian Development Bank and Energy Absolute have collaborated on a $48 million green loan to support Thailand's electric vehicle charging network.
Meanwhile, Malaysia has unveiled its National Low Carbon Cities 2030 plan, which involves establishing 200 low-carbon cities across the country. This initiative is expected to significantly drive the transition to green transportation, including electric vehicles. Malaysia also plans to deploy 25,000 public charging stations and 100,000 private charging stations by 2030, further bolstering the infrastructure for electric vehicle adoption.
As China's urban centers continue to expand, the government has embarked on initiatives to curb traffic pollution and reduce the nation's reliance on hydrocarbon imports while simultaneously fostering economic growth. China, known as the world's largest producer and consumer of electric vehicles (EVs), has implemented national sales targets, favorable legislation, promotional incentives, and urban climate plans to bolster domestic demand.
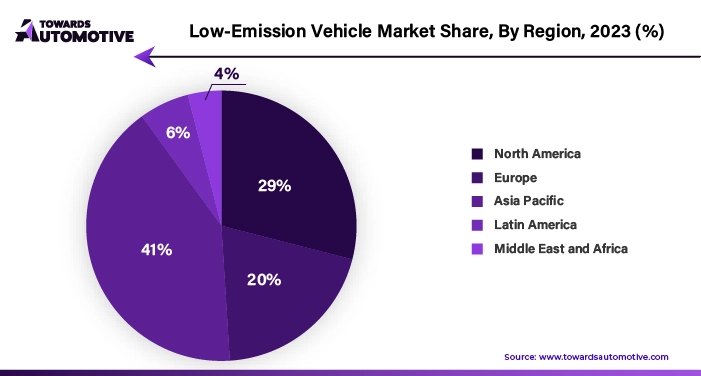
The electric vehicle industry in China stands as the largest globally, with production expected to surge by 1.6 times compared to the previous year, reaching an impressive 3.5 million units in 2021. With an annual revenue estimated at around US$102.2 billion, the electric vehicle sector boasts the highest revenue in the Asia-Pacific region.
China has implemented quotas mandating that manufacturers produce a minimum of 10% of all new vehicle sales as either 100% electric or hybrid vehicles. Furthermore, certain cities and provinces have imposed even stricter regulations. For instance, Beijing issues only 10,000 domestic licenses for electric cars each month, incentivizing residents to transition to electric vehicles. These measures have resulted in China establishing a robust and dependable electric vehicle production ecosystem, poised to drive further market growth.
The continual refinement of government regulations has spurred increased adoption of electric vehicles and facilitated the expansion of original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers. The region's contribution to the burgeoning demand in China's automotive industry is anticipated to fuel economic growth in the foreseeable future.
China's government actively encourages the adoption of electric vehicles, with plans already in place to phase out diesel usage in current-generation tractors and construction equipment. Moreover, China has set ambitious targets to entirely prohibit diesel and gasoline vehicles by the year 2040.
In recent years, Shenzhen has emerged as a significant player in the electric vehicle market, exporting nearly 60,000 electric trucks and urban vehicles, constituting approximately 35% of the city's urban transport fleet. With these developments, the market for low-volume vehicles is poised for growth during the forecast period.
The low-end car market is characterized by a diverse landscape comprising both well-established automotive giants and nimble startups, with an increasing number of regional players focusing on specific geographic areas. Among the notable participants, BYD emerges as a pivotal player, capitalizing on the growing demand for passenger cars and electric buses in both domestic and international markets. In 2018, BYD achieved a remarkable milestone by selling 227,152 passenger cars, securing the top position among all manufacturers in China. Additionally, BYD secured a substantial order for the construction of 4,473 electric buses for Guangzhou City, contributing to a total of 4,810 electric buses under this tender. Other major contenders in this market include Tesla, Daimler, Volkswagen AG, Toyota Motor Corp., Ford, and the Geely Group.
In a strategic move, the Italian Ministry of Economic Development unveiled a noteworthy initiative in April 2022, allocating 650 million Euros ($699 million) annually for the years 2022-2023-2024. This initiative is embedded within the framework of the federal budget allocation for the automotive sector, extending until 2030. The substantial financial contribution amounts to 8.7 billion euros ($9.34 billion). Notably, the incentives associated with this initiative for the purchase of electric, hybrid, plug-in, and endothermic vehicles are exclusively earmarked for individual consumers. Furthermore, a portion of these funds is designated to support ride-sharing companies in acquiring electric, hybrid, and plug-in vehicles.
Meanwhile, the Canadian government has embarked on an ambitious policy, launched in May 2022, with the objective of ensuring that all new cars sold in the country are Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEVs) by the year 2035. Under this initiative, the government has committed an investment of 529 million Canadian dollars (equivalent to 423 million US dollars), further underscoring its commitment to advancing the adoption of electric vehicles and fostering sustainability in the automotive sector.

Low-Emission Vehicle Market Recent Developments
A low-emission vehicle, often abbreviated as LEV, refers to a motor vehicle designed to emit significantly lower levels of pollutants from its engine compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. These vehicles are engineered to minimize the release of harmful gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere, thereby reducing their environmental impact.
The primary focus of low-emission vehicles is to mitigate emissions of pollutants such as nitrous oxide (NOx) and carbon dioxide (CO2), both of which are major contributors to air pollution and climate change. By employing advanced emission control technologies and alternative propulsion systems, low-emission vehicles strive to achieve cleaner and more sustainable transportation solutions.
Through the adoption of cleaner fuel sources, improved engine efficiency, and the use of emissions control devices such as catalytic converters and particulate filters, low-emission vehicles aim to minimize their environmental footprint while still providing efficient and reliable transportation options for consumers.
These vehicles play a crucial role in efforts to combat air pollution, mitigate climate change, and promote environmental sustainability in the transportation sector. By reducing emissions of harmful pollutants, low-emission vehicles contribute to cleaner air quality, healthier communities, and a more sustainable future for generations to come.
By Vehicle Type
Passenger Car
Commercial Vehicles
By Type
Hybrid
Mild Hybrid
Pure Electric Vehicle
By Geography
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025
We offer automotive expertise for market projections and customizable research, adaptable to diverse strategic approaches.
Contact Us